What are Vaginal Warts?
Definition and Overview
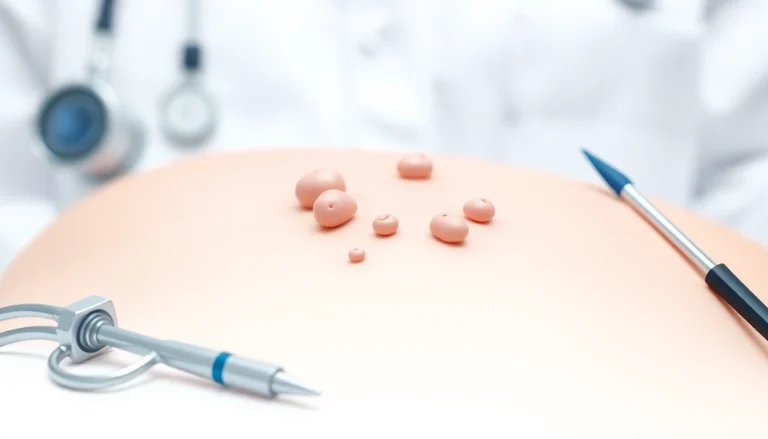
Vaginal warts, which are also known as genital warts, are small growths or lumps that occur in the genital area due to the human papillomavirus (HPV). These warts may manifest on the labia, inside the vagina, or around the anal region. While often asymptomatic, they can cause discomfort and may lead to emotional and psychological distress due to their nature and association with a sexually transmitted infection (STI). Understanding the complexities of Vaginal warts is essential for prevention, early detection, and effective treatment.
Causes of Vaginal Warts
The primary cause of vaginal warts is the human papillomavirus (HPV), particularly types 6 and 11, which are known for causing benign lesions. HPV is a sexually transmitted infection that can be transmitted through skin-to-skin contact during vaginal, anal, or oral intercourse. Vulnerability to HPV infection increases with multiple sexual partners, early onset of sexual activity, and a compromised immune system. Additionally, not all individuals infected with HPV will develop warts, as the immune system can suppress the virus in many cases.
How Vaginal Warts Develop
Once HPV enters the body, it typically resides in the skin and mucous membranes. Vaginal warts can take weeks or even months to develop after initial exposure to the virus. They may first appear as small, flesh-colored bumps, which can grow in size or multiply, forming larger clusters that resemble cauliflower. These growths are usually painless but can cause itching or other discomfort if irritated.
Symptoms Associated with Vaginal Warts
Common Visible Signs
Identifying vaginal warts can be straightforward, given their distinctive appearance. Common visible signs include:
- Small, flesh-colored or gray growths in and around the genital area
- Warts that may appear flat or have a raised, bumpy texture
- Clusters of warts that can form larger shaped lesions
Signs of Associated Conditions
It’s important to note that not all lumps or bumps in the genital area are vaginal warts. Other conditions such as vaginal skin tags, yeast infections, or even more serious concerns like sexually transmitted infections should be assessed. Symptoms to watch for may include:
- Severe itching or irritation in the genital area
- Unusual discharge
- Bleeding from the genital area without an apparent cause
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you suspect you have vaginal warts or experience symptoms such as pain or persistent irritation, it’s important to seek medical advice. Early diagnosis and intervention can help manage the condition effectively and reduce the risk of transmission to sexual partners.
Diagnosis of Vaginal Warts
Medical Examination Procedures
Diagnosing vaginal warts typically begins with a thorough examination by a healthcare provider. A visual inspection is generally sufficient when diagnosing external warts. In some cases, a healthcare professional may conduct additional examinations, such as a pelvic exam, to assess any internal warts.
Testing for Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
For individuals without visible warts, doctors may recommend HPV testing, especially for those with abnormal Pap smear results. HPV tests can detect the types of HPV that are most likely to cause cervical cancer, which may also be related to the presence of genital warts.
Interpreting Test Results
Positive test results for HPV indicate an infection, but it does not automatically mean that warts will develop. In many cases, the body’s immune system can suppress the virus. Healthcare providers can guide on monitoring and possible treatment options depending on individual circumstances.
Treatment Options for Vaginal Warts
Over-the-Counter Treatments
There are a few over-the-counter options available for the treatment of vaginal warts. These include topical creams that contain ingredients targeted at wart removal. It’s important to use these products strictly as directed and to avoid applying them to the healthy tissue around the warts, as they can cause irritation.
Prescription Medications
Healthcare professionals may prescribe stronger topical agents such as imiquimod or podofilox, which promote the immune system’s natural response to the HPV infection. Other prescription medications may include trichloroacetic acid (TCA) applied directly to the warts by a healthcare provider.
Professional Medical Procedures
For stubborn or extensive warts, professional medical procedures may be necessary. Options include:
- Cryotherapy: Freezing the warts with liquid nitrogen to destroy the tissue.
- Electrosurgery: Using electrical currents to burn off the warts.
- Laser Therapy: High-intensity light used to remove warts, particularly when they are widespread.
Preventive Measures Against Vaginal Warts
Vaccination and HPV Prevention
The HPV vaccine is a key preventive measure that protects against the most common cancer-causing types of HPV and also those likely to cause genital warts. Vaccination is recommended for preteens but can be administered up to the age of 45. Regular updates on vaccination status and effectiveness are essential to maintain long-term protection.
Safe Practices for Sexual Health
To reduce the risk of contracting or spreading HPV, individuals should adopt safe sexual practices, including:
- Consistent use of condoms can help lower the risk but not eliminate it completely, as HPV can infect areas not covered by condoms.
- Limit the number of sexual partners to reduce exposure risk.
- Engage in open and honest discussions with partners about sexual health and STI history.
Regular Health Check-Ups
Regular gynecological exams and Pap smears are important for monitoring reproductive health and detecting any abnormalities early. Regular screening helps ensure timely intervention and reduces complications related to HPV and other sexually transmitted infections.