In today’s fast-paced world, stress has become an unavoidable part of life. Many individuals often find themselves grappling with various stressors that can affect their mental and physical well-being. Understanding how to manage this stress is crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. This guide explores effective strategies for dealing with stress, from understanding what stress is to creating a personalized stress management plan.
Understanding Stress: What It Is and How It Affects Us
Defining Stress: The Basics
Stress is often defined as a state of mental or emotional strain resulting from adverse or demanding circumstances. It is a response to a challenge or demand, and our body reacts in certain ways. When we perceive a threat—what psychologists term a “stressor”—our body activates its stress response, leading to the release of hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol.
The Physical and Emotional Impacts of Stress
Stress can manifest in numerous ways, affecting both the body and mind. Physically, stress can lead to symptoms like headaches, muscle tension, fatigue, and digestive issues. Emotionally, it can contribute to feelings of anxiety, depression, and irritability. Understanding these impacts can help individuals realize the importance of addressing stress proactively.
Identifying Your Personal Stress Triggers
Identifying the specific events or situations that trigger stress is the first step in managing it effectively. These triggers can vary greatly from person to person and may include work pressures, relationship issues, and financial concerns. Keeping a stress diary can be an effective way for individuals to recognize what leads to their stress and how they respond to various stressors.
Common Symptoms of Stress and Their Implications
Recognizing Physical Symptoms of Stress
Some common physical symptoms of stress include:
- Headaches or migraines
- Fatigue or low energy
- Muscle tension or pain
- Sleep disturbances
- Digestive issues
Being aware of these symptoms is crucial, as they can serve as warnings from the body that stress levels are becoming unmanageable.
Emotional Responses: How Stress Manifests
Emotionally, stress can trigger a myriad of responses such as:
- Anxiety or worry
- Irritability or anger
- Feeling overwhelmed
- Depression or sadness
These emotional responses can further complicate life by impairing judgment and decision-making, creating a cycle of stress that can be difficult to break.
Long-Term Effects of Untreated Stress
If left untreated, stress can lead to serious long-term effects, including:
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Chronic respiratory problems
- Obesity and diabetes
- Gastrointestinal issues
- Increased risk of mental health disorders
Recognizing the long-term impact emphasizes the importance of managing stress before it escalates into more severe health issues.
Effective Techniques for Dealing with Stress
Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices for Stress Relief
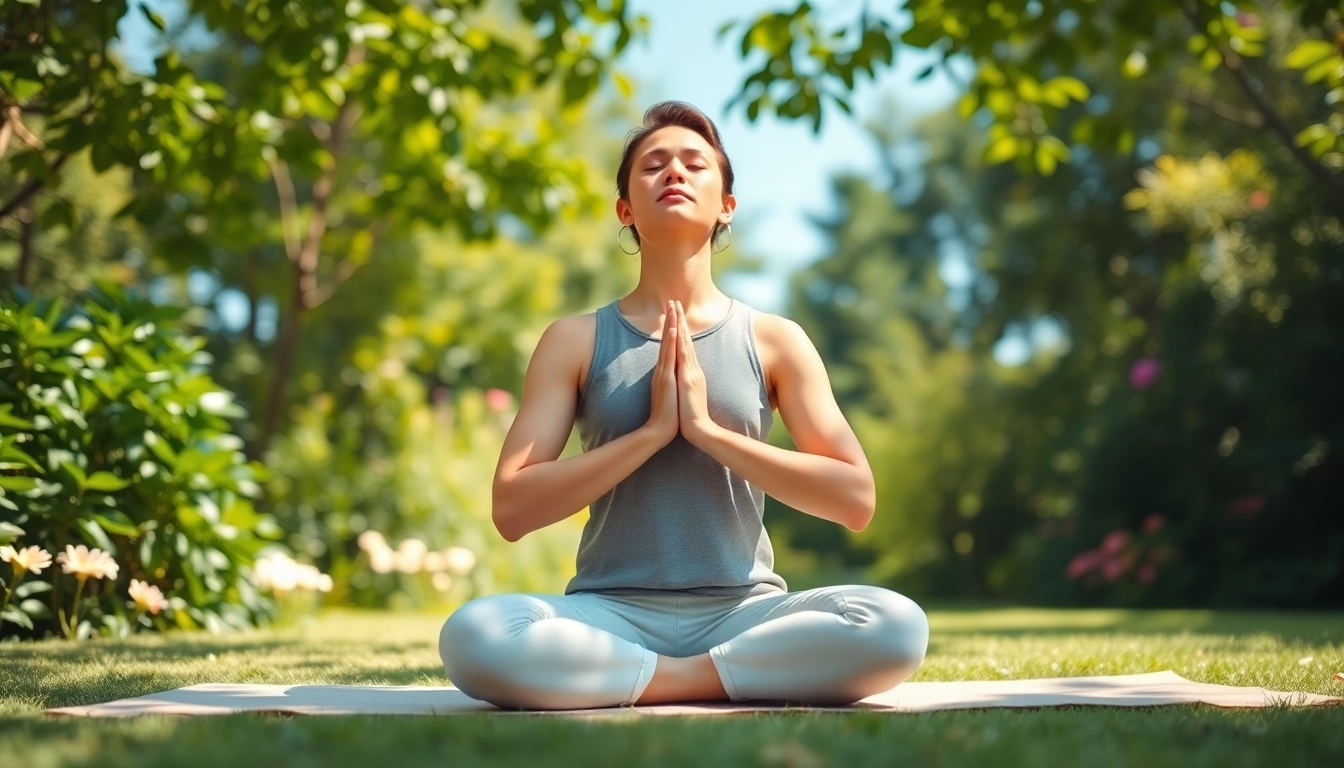
Mindfulness involves focusing on the present moment without judgment. This practice can help individuals gain better control over their thoughts and feelings. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and guided imagery can significantly reduce stress levels.
For instance, dedicating just five to ten minutes a day to mindfulness practices can offer profound benefits, helping to alleviate anxiety and improve overall mental clarity.
Physical Activity: The Role of Exercise in Stress Management
Exercise is one of the most effective stress relievers. Engaging in physical activity releases endorphins, the body’s natural feel-good hormones. Regular exercise can improve both physical health and mental well-being.
Activities such as yoga, walking, and strength training can also serve as an outlet for pent-up energy and tension, promoting relaxation and mental peace.
Healthy Eating and Lifestyle Choices
Nutrition plays a key role in stress management. A well-balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, supports a healthy body and mind, while reducing stress levels. Avoiding caffeine, alcohol, and sugar can also help stabilize mood and energy levels.
Developing a Personal Stress Management Plan
Setting Realistic Goals for Stress Reduction
Creating achievable goals is crucial in managing stress. Such goals should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) to ensure they are clear and actionable. For example, instead of setting a vague goal of “reducing stress,” aim for “practicing yoga twice a week for 30 minutes.”
Incorporating Daily Routine Changes
Making small adjustments to daily routines can dramatically influence stress levels. Simple changes, such as setting aside quiet time for yourself, organizing your workspace, or establishing a sleep schedule, can enhance productivity and reduce feelings of overwhelm.
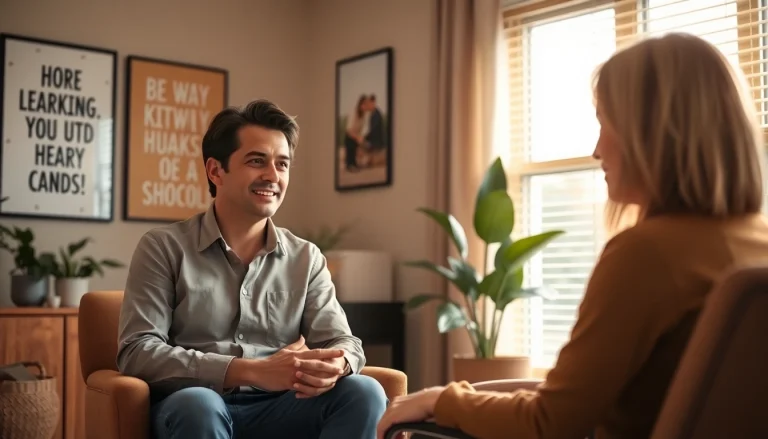
Seeking Professional Help When Necessary
If stress becomes unmanageable, seeking the help of a mental health professional can provide crucial support. Therapists, counselors, and psychologists can offer tailored strategies to cope with stress effectively and guide individuals in navigating their challenges.
Staying Resilient: Maintaining Low Stress Levels Over Time
Building a Supportive Network
Having a strong support system in place can help individuals navigate stress more effectively. Connect with friends, family, or support groups who understand your challenges, allowing you to share experiences and solutions to stress-related issues.
Continuous Learning and Adapting to Challenges
Resilience involves a commitment to lifelong learning. Embrace change and challenges as opportunities for growth rather than obstacles. Developing problem-solving skills, seeking out resources, and learning from experiences enhance resilience and reduce stress.
Evaluating Your Stress Management Success
Regularly assess the effectiveness of your stress management plan. This reflection can be done through journaling or simply taking time to review your actions and their outcomes. What worked? What didn’t? Fine-tuning your approach will help you sustain lower stress levels over time.
In conclusion, dealing with stress involves understanding its sources, recognizing symptoms, and employing practical strategies for management. By incorporating mindfulness practices, physical activity, healthy eating, and a support network, individuals can create a robust framework for reducing stress and enhancing overall well-being. Prioritizing stress management is not just an option; it’s a necessity for a balanced and fulfilling life.